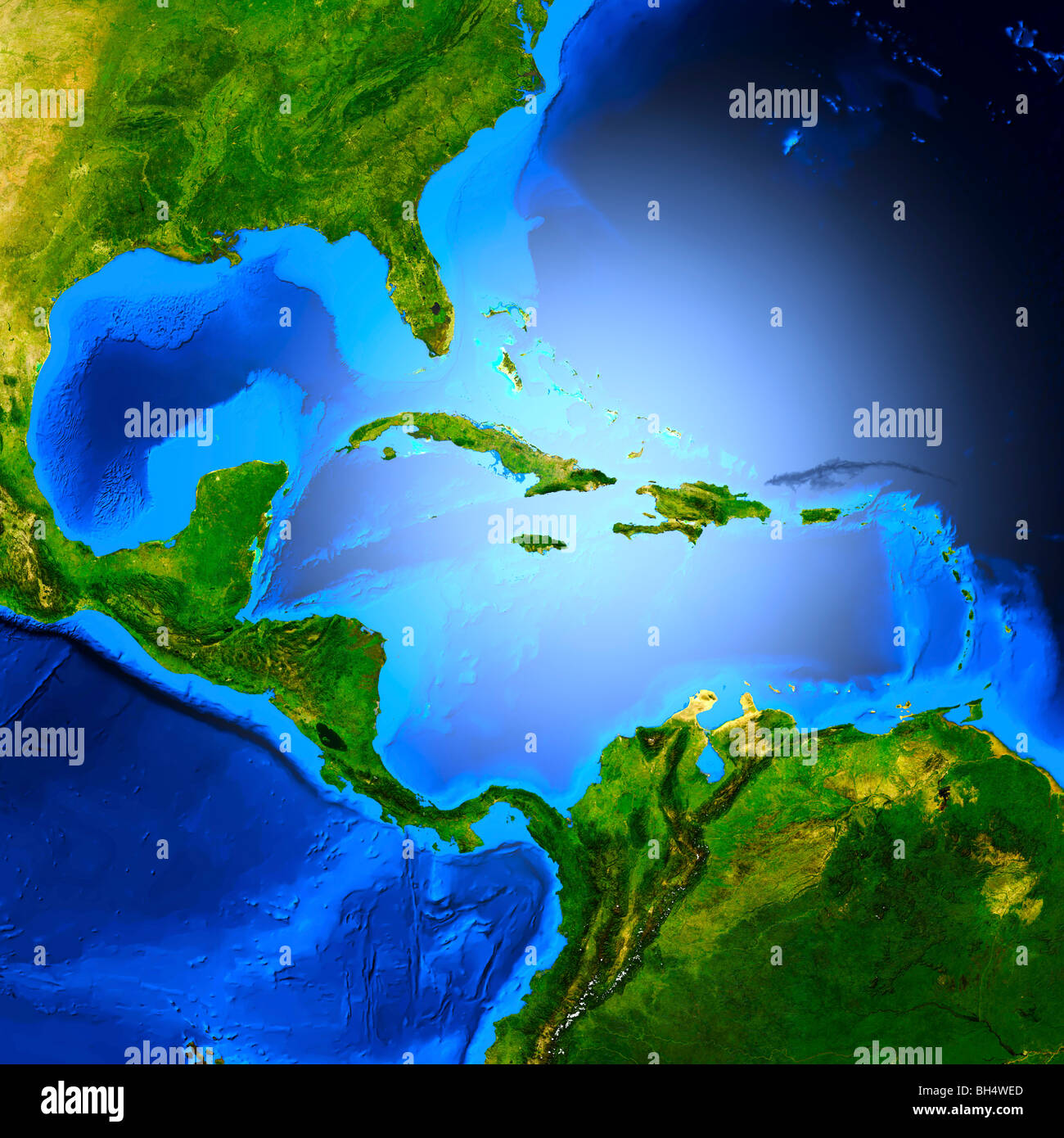
The Gulf of Mexico, often referred to as the Gulf of America, is a globally significant region that combines natural beauty with economic importance. Covering an expansive area of over 1.6 million square kilometers, this semi-enclosed sea plays a crucial role in international trade, energy production, and biodiversity conservation. Its strategic location and abundant resources have made it a focal point for scientists, policymakers, and businesses alike, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices to preserve its ecological and economic value.
The Gulf of Mexico serves as a natural boundary between the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, making it a crucial waterway for international commerce. As a gateway for trade between North America and other continents, it hosts numerous ports that facilitate the movement of goods and resources. Beyond its economic significance, the Gulf is home to a rich array of marine life, supporting a thriving fishing industry and drawing millions of tourists annually to its picturesque shores.
Despite its immense importance, the Gulf of Mexico encounters substantial environmental challenges, such as oil spills, habitat degradation, and the impacts of climate change. Safeguarding this vital resource necessitates collaborative efforts from governments, industries, and local communities. In this article, we will explore the geography, economy, ecology, and conservation initiatives related to the Gulf of Mexico, offering a comprehensive understanding of this extraordinary region.
Read also:Discovering Aj Storr A Deep Dive Into The Life And Legacy Of A Digital Icon
Table of Contents
- Geography of the Gulf of Mexico
- Economic Importance of the Gulf of America
- Biodiversity in the Gulf of Mexico
- Climate Change and Its Impact
- Oil Industry and Environmental Concerns
- Tourism and Recreational Activities
- Conservation Efforts in the Gulf
- Historical Significance of the Gulf
- Challenges Facing the Gulf of Mexico
- The Future of the Gulf of America
The Geographic Marvel of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a vast body of water that spans approximately 1.6 million square kilometers, ranking among the largest gulfs globally. It is bordered by the United States to the north, Mexico to the west, and Cuba to the southeast. The Gulf connects to the Atlantic Ocean via the Florida Straits and to the Caribbean Sea through the Yucatan Channel, establishing it as a critical link in the global maritime network.
Key Features of the Gulf
- Depth: The Gulf has an average depth of about 1,615 meters, with the Sigsbee Deep reaching a maximum depth of approximately 3,742 meters.
- Coastline: The Gulf boasts a diverse coastline, ranging from sandy beaches to marshlands and mangroves, supporting a wide array of ecosystems.
- Islands: Several islands, including the Florida Keys and the Chandeleur Islands, are scattered throughout the Gulf, providing essential habitats for wildlife.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the Gulf of Mexico is home to some of the world's most productive fisheries, with its warm waters nurturing a wide variety of marine species.
The Economic Backbone of the Gulf of America
The Gulf of Mexico is a cornerstone of the global economy, particularly in the domains of energy production, shipping, and fishing. This region is one of the largest producers of oil and natural gas, supplying a significant portion of the United States' energy requirements. Additionally, the Gulf's ports rank among the busiest in the world, enabling the efficient movement of goods and resources.
Energy Production
The Gulf of Mexico contributes approximately 17% of the total oil production in the United States, as reported by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. The region's extensive reserves of oil and natural gas have positioned it as a focal point for energy companies, driving economic growth and job creation.
Fishing Industry
The Gulf of Mexico sustains one of the largest fishing industries globally, with commercial fisheries generating billions of dollars in revenue annually. Species such as shrimp, oysters, and red snapper are highly sought-after, providing food for millions and supporting local economies.
The Rich Biodiversity of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a biodiversity hotspot, hosting thousands of marine species. From vibrant coral reefs to expansive sea grass beds, the region's ecosystems support a wide range of organisms, many of which are endemic to the area. The Gulf's warm waters and diverse habitats create an ideal environment for marine life to flourish.
Read also:Exploring The Drake Bulldogs A Comprehensive Look At The 20232024 Basketball Roster
Key Species
- Sea Turtles: Five of the seven species of sea turtles inhabit the Gulf, including the critically endangered Kemp's ridley turtle.
- Dolphins: Bottlenose dolphins are frequently observed in the Gulf, attracting tourists and researchers alike.
- Mangroves: These coastal trees provide critical habitat for fish, birds, and other wildlife while protecting shorelines from erosion.
A study published in the journal Marine Ecology Progress Series underscores the importance of preserving the Gulf's biodiversity, emphasizing the need for sustainable management practices to ensure the long-term health of its ecosystems.
The Impact of Climate Change on the Gulf
Climate change presents a significant threat to the Gulf of Mexico, with rising sea levels, increasing water temperatures, and more frequent storms affecting its ecosystems and communities. The Gulf's coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to these changes, as they are home to millions of people and support vital industries.
Sea Level Rise
As per the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), sea levels in the Gulf of Mexico are projected to rise by up to one meter by the end of the century, endangering low-lying areas with flooding and erosion. This could have catastrophic consequences for coastal communities, infrastructure, and wildlife habitats.
Temperature Increase
The warming of Gulf waters contributes to the bleaching of coral reefs and the migration of fish species to cooler waters. This disruption could destabilize the region's ecosystems, impacting the fishing industry and tourism sector.
Environmental Concerns in the Oil Industry
The oil industry is a major economic driver in the Gulf of Mexico but also poses significant environmental risks. Events like the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010 have caused extensive damage to marine life and coastal ecosystems. Preventing and mitigating such incidents is crucial to protecting the Gulf's natural resources.
Prevention Measures
- Implementing enhanced safety standards and regulations for offshore drilling operations.
- Investing in cutting-edge technology for detecting and responding to oil spills.
- Promoting collaboration between governments, industries, and communities to develop comprehensive emergency response plans.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues to work with stakeholders to enhance safety measures and minimize the environmental impact of oil production in the Gulf.
The Role of Tourism and Recreation
The Gulf of Mexico welcomes millions of tourists each year, captivated by its stunning beaches, vibrant culture, and diverse recreational opportunities. Activities such as fishing, boating, and diving are immensely popular among visitors, contributing to the region's economy and fostering environmental awareness.
Ecotourism
Ecotourism is gaining traction in the Gulf, as travelers seek to experience the region's natural beauty while supporting conservation efforts. Programs focused on marine life observation, habitat restoration, and sustainable fishing practices are instrumental in raising awareness about the importance of protecting the Gulf's ecosystems.
Conservation Initiatives in the Gulf
Protecting the Gulf of Mexico requires a comprehensive approach involving government agencies, non-profit organizations, and local communities. Efforts aimed at reducing pollution, restoring habitats, and promoting sustainable practices are vital to ensuring the long-term health of the region.
Habitat Restoration
- Replanting mangroves and sea grass to provide critical habitat for marine life.
- Restoring wetlands to mitigate storm surges and reduce erosion.
- Establishing marine protected areas to safeguard vulnerable species and ecosystems.
Organizations such as the Gulf Coast Ecosystem Restoration Council (RESTORE) are actively implementing projects to address the environmental challenges facing the Gulf, prioritizing long-term sustainability.
The Historical Legacy of the Gulf
The Gulf of Mexico has played a pivotal role in the history of the Americas, serving as a vital waterway for exploration, trade, and settlement. From the early Spanish explorers to the modern-day oil industry, the Gulf has been central to many significant events that have shaped the region's development.
Exploration and Colonization
In the 16th century, Spanish explorers like Hernando de Soto and Pánfilo de Narváez ventured into the Gulf, establishing settlements and mapping the coastline. These pioneering expeditions laid the foundation for the colonization of the Americas, with the Gulf serving as a key transportation route for goods and people.
The Challenges Ahead for the Gulf of Mexico
Despite its significance, the Gulf of Mexico confronts numerous challenges that threaten its ecological and economic well-being. Issues such as pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change demand immediate attention and action to prevent further degradation of the region.
Water Pollution
Agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban development contribute to the pollution of the Gulf's waters, leading to the formation of dead zones where marine life cannot survive. Addressing these sources of pollution is critical to restoring the health of the Gulf's ecosystems.
The Future of the Gulf of America
The future of the Gulf of Mexico hinges on the actions taken today to protect its resources and promote sustainable development. By embracing innovative technologies, strengthening regulations, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can ensure that the Gulf remains a vital and vibrant region for future generations.
In summary, the Gulf of Mexico, or Gulf of America, is a remarkable region that plays an indispensable role in the global economy and environment. Its rich biodiversity, strategic location, and abundant resources make it an invaluable asset, yet it faces significant challenges that require our attention and action. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below and to explore our other articles for further insights into this captivating region.