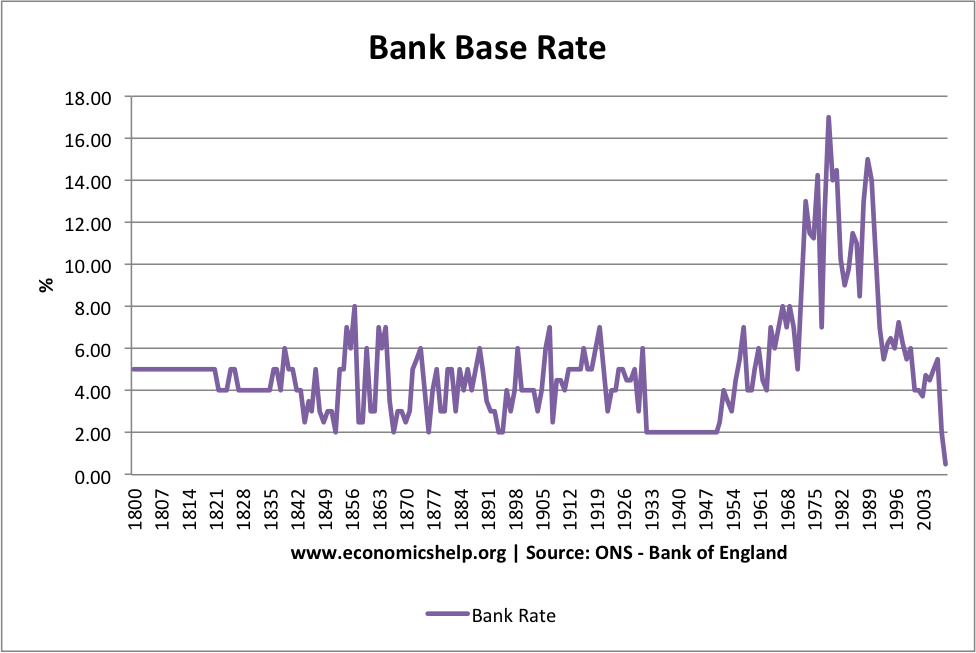
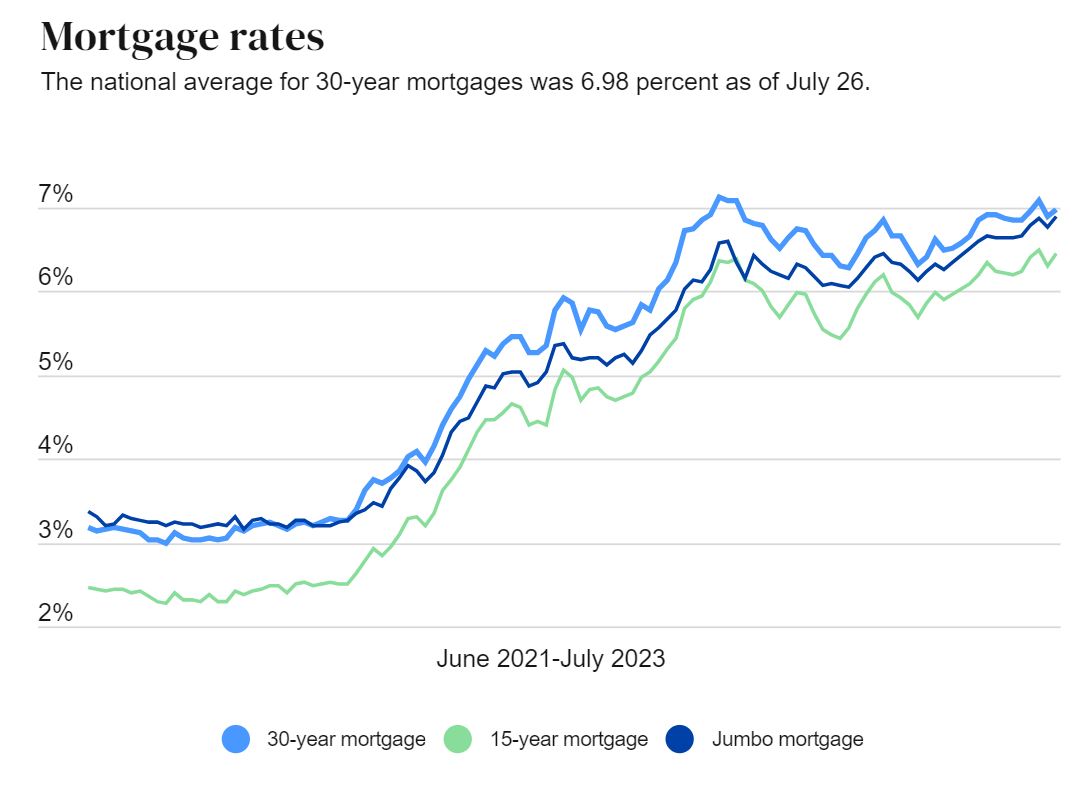
Interest rates serve as one of the most influential elements in the financial ecosystem, shaping everything from borrowing expenses to investment strategies. Whether you're depositing funds into a savings account, securing a mortgage, or investing in bonds, having a solid grasp of how interest rates operate is vital. They function as the cost of borrowing money and play an instrumental role in steering economic growth, managing inflation, and guiding monetary policy.
For both individuals and businesses, interest rates dictate the expense of capital and the return on savings. As global economies continue to transform, staying updated about these rates becomes increasingly significant. This article will delve into the concept of interest rates in detail, covering their types, their influence on the economy, and strategies to handle them effectively.
By the conclusion of this guide, you'll possess a comprehensive understanding of how interest rates influence your financial choices and how you can utilize them to meet your objectives. Let's embark on an exploration of the intricate world of interest rates.
Read also:Exploring The Distinct Charm Of Montana And Wisconsin
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Concept of Interest Rates
- Various Types of Interest Rates
- Key Factors Influencing Interest Rates
- The Role of Interest Rates in Economic Dynamics
- Central Banks: The Architects of Interest Rate Policies
- Understanding Real and Nominal Interest Rates
- The Interplay Between Interest Rates and Inflation
- Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
- Analyzing Current Interest Rate Trends
- Final Thoughts
Exploring the Concept of Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the percentage charged or earned on borrowed or lent money, acting as the cost of borrowing or the reward for lending. They serve as a foundational mechanism in financial markets, influencing consumer actions, business strategies, and government policies. For instance, when you secure a loan, the interest rate determines the additional amount you'll repay over time.
Beyond loans, interest rates apply to savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and various investment vehicles. They function as a balancing tool between the supply and demand for money, ensuring liquidity and stability in the economy. A thorough understanding of interest rates is essential for anyone aiming to make well-informed financial decisions.
Various Types of Interest Rates
1. Prime Interest Rate
The prime interest rate is the lowest rate at which banks extend loans to their most creditworthy clients. It serves as a benchmark for other interest rates, such as those for mortgages and credit cards. Typically, only large corporations or affluent individuals qualify for loans at the prime rate.
2. Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates remain unchanged throughout the duration of a loan or investment, offering stability and predictability. In contrast, variable interest rates fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially resulting in higher or lower costs over time. Borrowers should thoughtfully assess their financial circumstances before opting for fixed or variable rates.
3. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Interest Rates
Short-term interest rates apply to loans or investments lasting less than a year, whereas long-term rates cover periods exceeding one year. The disparity between these rates can provide insights into the overall health of the economy and investor sentiment.
Key Factors Influencing Interest Rates
A multitude of factors shape interest rates, both domestically and internationally. These include:
Read also:Understanding Vix A Comprehensive Guide To Market Volatility
- Economic Growth: Robust economic growth often leads to higher interest rates as the demand for borrowing rises.
- Inflation: Central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation, raising them when prices escalate too rapidly.
- Monetary Policy: Decisions by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S., significantly influence benchmark interest rates.
- Government Debt: Excessive government borrowing can elevate interest rates as investors seek higher returns to compensate for increased risk.
Understanding these factors enables individuals and businesses to anticipate interest rate fluctuations and plan effectively.
The Role of Interest Rates in Economic Dynamics
1. Consumer Spending
Lower interest rates stimulate consumer spending by reducing the cost of borrowing for significant purchases, such as homes, vehicles, and appliances. Conversely, higher interest rates can curb spending as borrowing becomes more expensive.
2. Business Investment
Interest rates also impact business investment decisions. Lower rates make borrowing more affordable for companies seeking to expand or initiate new projects, while higher rates may lead to reduced investment.
3. Exchange Rates
Interest rates influence exchange rates by affecting the flow of capital into and out of a country. Higher rates attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency, while lower rates may lead to currency depreciation.
Central Banks: The Architects of Interest Rate Policies
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, hold a central role in determining interest rates. Through monetary policy instruments like open market operations and reserve requirements, they strive to maintain economic stability, control inflation, and foster employment.
For example, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate growth. Conversely, during periods of high inflation, they may raise rates to temper economic activity.
Understanding Real and Nominal Interest Rates
Nominal interest rates reflect the stated rate of interest on a loan or investment, while real interest rates account for inflation. The real interest rate provides a more accurate representation of the true borrowing cost or savings return.
Formula: Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation Rate
Investors and borrowers should consider real interest rates when evaluating financial opportunities to ensure they're making well-informed decisions.
The Interplay Between Interest Rates and Inflation
Inflation and interest rates share a close relationship, with central banks utilizing interest rates as a tool to manage inflation. When inflation surges, central banks typically raise interest rates to curtail spending and borrowing, thereby slowing down the economy. Conversely, during periods of low inflation or deflation, they may lower rates to encourage economic activity.
Historical evidence indicates that maintaining equilibrium between inflation and interest rates is critical for long-term economic stability. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), countries with consistent interest rate policies tend to experience more predictable economic growth.
Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
1. Diversification
Investors can mitigate interest rate risk by diversifying their portfolios across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. This approach helps shield against the impact of interest rate fluctuations on specific investments.
2. Hedging Strategies
Hedging entails using financial instruments like futures or options to counterbalance potential losses caused by interest rate changes. Businesses and investors frequently employ hedging strategies to protect against unfavorable market conditions.
3. Monitoring Economic Indicators
Staying abreast of economic indicators, such as employment statistics, GDP growth, and inflation rates, can assist individuals and businesses in predicting interest rate movements and adjusting their strategies accordingly.
Analyzing Current Interest Rate Trends
As of 2023, global interest rates exhibit signs of volatility due to ongoing economic challenges, including inflationary pressures and geopolitical tensions. The Federal Reserve, for instance, has implemented several rate hikes to combat rising prices, while other central banks have adopted similar measures.
Experts anticipate that interest rates may remain elevated in the near future as central banks work toward achieving their inflation targets. However, the exact path will depend on various factors, including global economic conditions and policy decisions.
Final Thoughts
Interest rates form the bedrock of the financial system, influencing everything from personal savings to global economic policies. By comprehending the diverse types of interest rates, the factors affecting them, and their impact on the economy, individuals and businesses can make more informed financial decisions.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from understanding interest rates. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or question below, and we'll be delighted to assist you further. Stay tuned for more insightful content on financial topics!
![Buying a Home? Mortgage Rate Guide for Singapore [2023]](https://blog.roshi.sg/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Singapore-Home-Loan-Rates-2022.jpeg)