Dengue fever is a significant mosquito-borne illness that impacts millions globally each year. This viral infection can escalate to life-threatening conditions if not treated promptly. As the world continues to confront infectious diseases, it’s essential to gain a deeper understanding of dengue fever, its symptoms, prevention techniques, and treatment options.
Dengue fever has become a mounting public health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Caused by the dengue virus, it spreads through the bites of infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Since there is no specific cure, early detection and appropriate management are vital to prevent severe complications.
In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options for dengue fever. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to safeguard yourself and your loved ones from this perilous disease.
Read also:Discover The Rich Legacy Of North Carolina Basketball
Table of Contents
- Understanding Dengue Fever
- Root Causes of Dengue Fever
- Identifying Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Diagnosing Dengue Fever
- Managing Dengue Fever
- Preventive Measures Against Dengue
- Exploring Dengue Vaccines
- Global Impact of Dengue Fever
- Emerging Research on Dengue
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a viral disease primarily transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito. It is widespread in over 100 countries, particularly in Asia, the Pacific, the Americas, and Africa. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 390 million dengue infections occur annually, with around 96 million showing clinical symptoms.
This disease comprises four distinct serotypes, which means infection with one serotype does not confer immunity against the others. In fact, subsequent infections with different serotypes can heighten the risk of developing severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever.
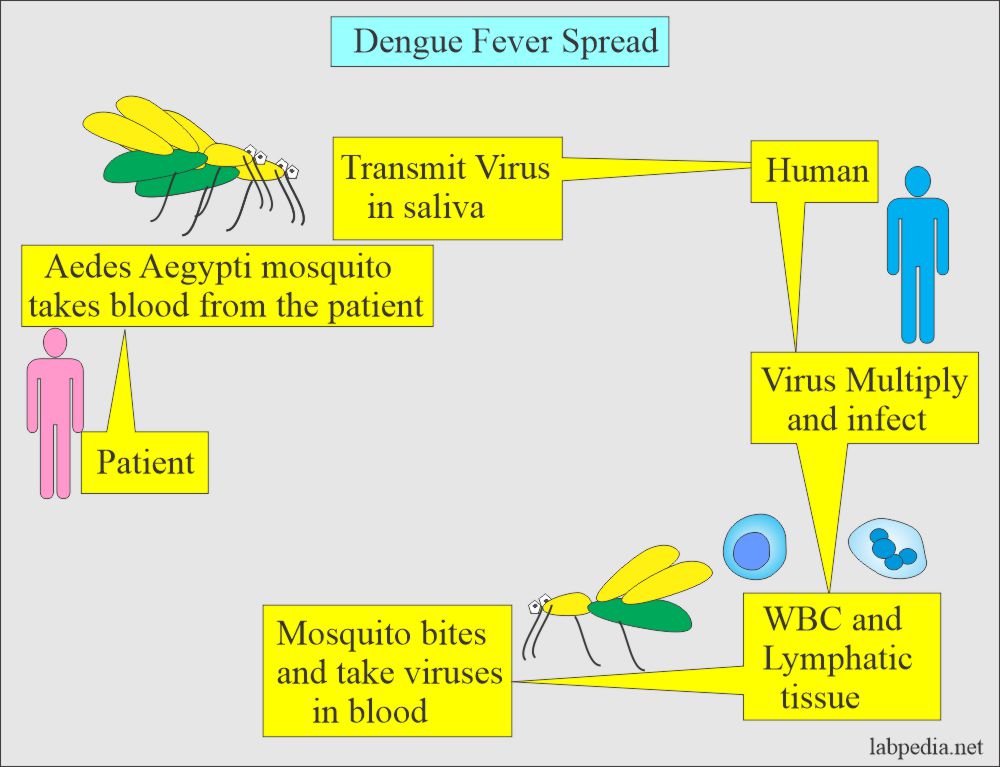
Understanding the Transmission Cycle
The transmission cycle of dengue fever involves two primary hosts: humans and mosquitoes. When an Aedes aegypti mosquito bites a person infected with the dengue virus, it becomes a carrier. The virus then multiplies within the mosquito, enabling it to transmit the disease to other individuals through subsequent bites.
Root Causes of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, which belongs to the Flavivirus genus. This virus is predominantly transmitted through the bites of infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Urbanization, globalization, and climate change have facilitated the spread of this disease by creating environments conducive to mosquito breeding.
Factors Contributing to Dengue Spread
- Inefficient waste management leading to stagnant water accumulation
- Increased international travel and trade facilitating the spread of infected mosquitoes
- Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns due to climate change
Identifying Symptoms of Dengue Fever
The symptoms of dengue fever typically manifest between 4 to 10 days after infection. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include high fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, rash, and mild bleeding.
In severe cases, dengue fever can evolve into dengue hemorrhagic fever, characterized by bleeding, plasma leakage, and a low platelet count. This condition necessitates immediate medical attention to avert complications.
Read also:John Calipari A Comprehensive Look At The Legendary Coach
Diagnosing Dengue Fever
Diagnosing dengue fever involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers assess the patient’s symptoms, travel history, and exposure to mosquitoes. Laboratory tests such as NS1 antigen detection, IgM antibody testing, and PCR can confirm the presence of the dengue virus.
Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of dengue fever is critical for effective management. Since symptoms often resemble other viral infections, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you reside in or have recently visited an endemic area and experience fever and associated symptoms.
Managing Dengue Fever
There is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue fever. Treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Patients are advised to rest, stay hydrated, and take acetaminophen to reduce fever and pain. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to monitor and manage complications such as fluid loss, bleeding, and organ dysfunction.
Preventive Measures Against Dengue
Preventing dengue fever involves controlling mosquito populations and reducing human exposure to mosquito bites. Key prevention strategies include:
- Eliminating standing water where mosquitoes can breed
- Using mosquito nets and screens on windows and doors
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and using insect repellents
Community Involvement in Prevention
Community participation is vital in combating dengue fever. Public awareness campaigns, regular clean-up drives, and collaboration with local health authorities can significantly reduce the risk of dengue outbreaks.
Exploring Dengue Vaccines
Several dengue vaccines have been developed to protect against the disease. The most widely used vaccine, Dengvaxia, is approved for individuals aged 9 to 45 years living in endemic areas. However, its efficacy depends on prior dengue infection history, and it is not recommended for people who have never been infected with the virus.
Challenges in Vaccine Development
Developing a universal dengue vaccine that offers protection against all four serotypes remains a challenge. Researchers are actively exploring new vaccine candidates and enhancing existing ones to improve their efficacy and safety.
Global Impact of Dengue Fever
Dengue fever poses a substantial global health burden, with an estimated 3.9 billion people at risk of infection in over 129 countries. According to the WHO, the number of reported dengue cases has surged dramatically in recent decades, with the Americas, Southeast Asia, and Western Pacific regions being the most affected.
A 2021 study published in The Lancet estimated that dengue causes an economic burden of approximately $9 billion annually, underscoring the need for effective prevention and control measures.
Emerging Research on Dengue
Recent advancements in dengue research focus on understanding the virus’s biology, improving diagnostic tools, and developing novel treatments. Scientists are investigating antibody-based therapies, antiviral drugs, and genetic modifications of mosquitoes to reduce transmission.
Innovative Approaches to Combat Dengue
A promising approach involves the use of Wolbachia bacteria to infect mosquitoes, diminishing their ability to transmit the dengue virus. Field trials in several countries have demonstrated promising results, with significant reductions in dengue cases in treated areas.
Final Thoughts
Dengue fever continues to be a major public health challenge worldwide, affecting millions annually. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies is essential in combating this disease. While there is no specific cure, early diagnosis and proper management can significantly enhance outcomes.
We urge you to adopt preventive measures to protect yourself and your community from dengue fever. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about this critical health issue. For more information, explore our other articles on infectious diseases and public health topics.
References:
- World Health Organization. (2021). Dengue and severe dengue. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue
- Bhatt, S., et al. (2013). The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature, 496(7446), 504-507.
- The Lancet. (2021). The global economic burden of dengue illness. Retrieved from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(21)00084-5/fulltext