Interest rates are among the most crucial factors influencing financial decisions, ranging from borrowing money to investing in assets. Whether you're securing a mortgage, planning for retirement, or managing debt, having a solid understanding of how interest rates function is vital. This guide delves deeply into the world of interest rates, equipping you with the knowledge to make well-informed financial decisions.
In today's dynamic economy, fluctuations in interest rates can profoundly impact personal and business finances. Whether you're a homeowner, an investor, or a small business owner, staying informed about interest rates is essential for maintaining financial stability and fostering growth.
This article will explore everything you need to know about interest rates, including their definitions, various types, their influence on the economy, and strategies for managing them effectively. Let's start by examining the basics and why they matter to your financial well-being.
Read also:Aaron Paul The Journey Of A Hollywood Icon
Table of Contents
- What Are Interest Rates?
- Types of Interest Rates
- Factors Affecting Interest Rates
- Impact of Interest Rates on the Economy
- The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
- Interest Rates and Personal Finance
- How Interest Rates Affect Businesses
- Historical Trends in Interest Rates
- Future Outlook on Interest Rates
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
What Are Interest Rates?
Interest rates represent the percentage charged or paid on a loan or deposit. They signify the cost of borrowing money or the return on saving it. Essentially, interest rates are a fundamental component of the financial system, influencing everything from consumer spending to business investments.
Key points:
- Interest rates are typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR).
- They can be fixed or variable, depending on the terms of the loan or deposit.
- Interest rates affect both borrowers and lenders, shaping financial decisions and behaviors.
Why Are Interest Rates Important?
Interest rates play a critical role in the economy by influencing spending, saving, and investment decisions. For borrowers, lower interest rates mean reduced costs for loans, making it easier to finance significant purchases like homes or cars. On the other hand, higher interest rates encourage saving by providing better returns on deposits, thereby promoting financial prudence.
Types of Interest Rates
There are several types of interest rates, each serving distinct purposes within the financial system. Gaining a thorough understanding of these variations is crucial for effectively managing your finances.
Nominal Interest Rate
The nominal interest rate is the stated rate on a loan or deposit before adjusting for inflation. It reflects the basic cost of borrowing or the return on savings without accounting for external economic factors. This rate is often used as a starting point for financial calculations.
Real Interest Rate
The real interest rate adjusts the nominal rate for inflation, offering a more precise picture of the true cost of borrowing or return on savings. This rate is particularly important for long-term financial planning, as it accounts for the gradual erosion of purchasing power over time, ensuring that your savings retain their value.
Read also:Exploring The Potential Of Best Picture 2025 At The Academy Awards
Effective Interest Rate
The effective interest rate takes compounding into account, providing a more accurate representation of the total cost of borrowing or return on investment. It is often higher than the nominal rate due to the effects of compounding, making it a more reliable measure for evaluating the true cost of financial products.
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic conditions, monetary policy, and market demand. Below are some of the key factors that affect interest rates:
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to higher interest rates as the demand for loans increases, reflecting a robust and expanding economy.
- Inflation: Central banks adjust interest rates to control inflation, raising them when prices rise too quickly to maintain economic stability.
- Monetary policy: Central banks utilize interest rates as a tool to manage economic stability and growth, making them a critical lever in shaping economic conditions.
- Supply and demand: The availability of credit and the demand for loans also play a significant role in determining interest rates, influencing borrowing costs across the board.
Impact of Interest Rates on the Economy
Interest rates have a profound and far-reaching impact on the economy, influencing consumer behavior, business decisions, and government policies. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more affordable, stimulating spending and investment. Conversely, higher interest rates discourage borrowing, slowing economic activity and helping to reduce inflationary pressures.
How Interest Rates Affect Consumers
For consumers, interest rates directly influence the cost of borrowing for major purchases such as homes, cars, and education. Lower rates make these purchases more accessible and affordable, while higher rates increase the cost of financing, potentially delaying or discouraging significant financial commitments.
The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the European Central Bank, play a pivotal role in setting interest rates. They use monetary policy tools to adjust rates in response to economic conditions, aiming to maintain price stability and promote sustainable economic growth.
Monetary Policy Tools
Central banks employ a variety of tools to influence interest rates:
- Open market operations: Buying or selling government securities to adjust the money supply, influencing borrowing costs throughout the economy.
- Discount rate: The rate charged to commercial banks for borrowing from the central bank, impacting the cost of credit in the financial system.
- Reserve requirements: The amount of funds banks must hold in reserve, affecting their ability to lend and, consequently, influencing interest rates.
Interest Rates and Personal Finance
Interest rates have a direct and significant impact on personal finance decisions, affecting everything from savings accounts to credit card debt. Developing a clear understanding of how interest rates work can empower you to make smarter financial choices, optimizing your financial well-being.
Tips for Managing Interest Rates
Here are some strategies for managing interest rates effectively:
- Lock in fixed rates: Secure fixed rates for long-term loans when rates are low to protect yourself from future increases.
- Pay off high-interest debt: Prioritize paying off high-interest debt quickly to minimize costs and improve your financial health.
- Shop around: Compare rates on savings accounts and loans to ensure you're getting the best possible terms and maximizing your returns.
How Interest Rates Affect Businesses
Businesses are significantly influenced by interest rates, as they affect the cost of borrowing for expansion, equipment purchases, and working capital. Lower interest rates make it easier for businesses to access financing, facilitating growth and innovation. Conversely, higher rates can restrict growth opportunities, necessitating careful financial planning and management.
Strategies for Businesses
To mitigate the impact of fluctuating interest rates, businesses can adopt the following strategies:
- Hedge against interest rate risk: Use financial instruments to protect against potential increases in interest rates, ensuring financial stability.
- Lock in favorable rates: Secure long-term financing agreements at favorable rates to safeguard against future rate hikes.
- Improve cash flow management: Focus on optimizing cash flow to reduce reliance on borrowing, enhancing financial flexibility and resilience.
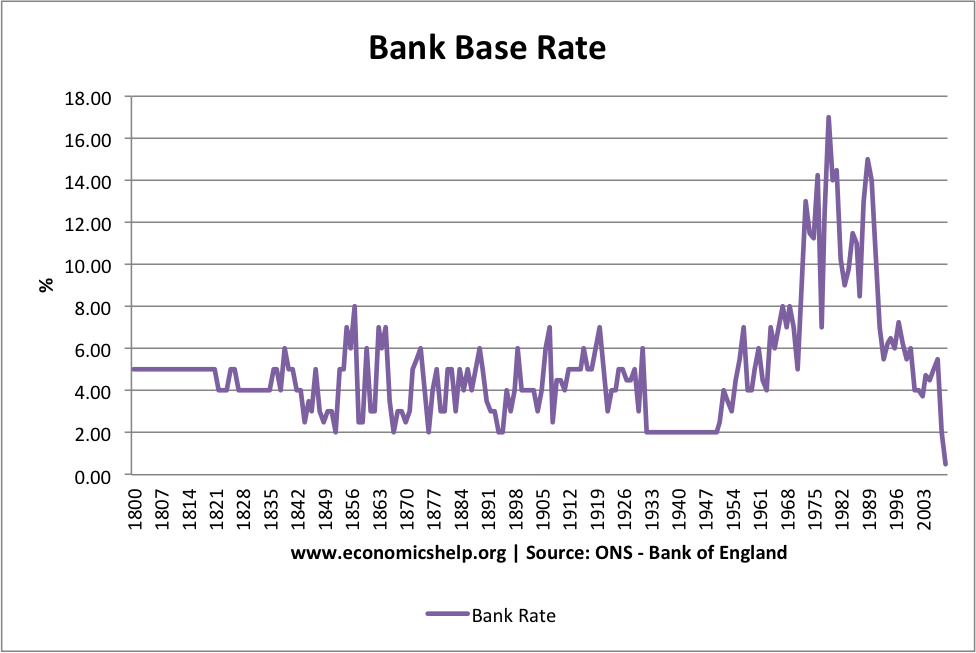
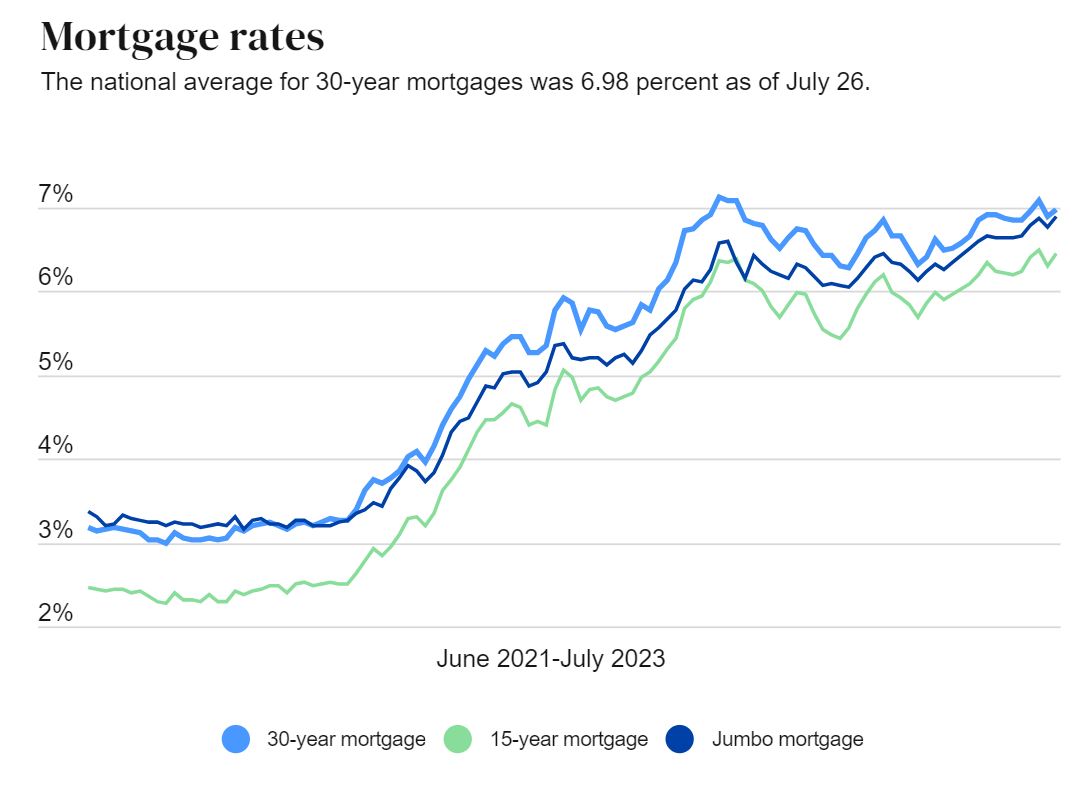
Historical Trends in Interest Rates
Interest rates have experienced significant fluctuations over the years, reflecting changes in economic conditions and monetary policy. For instance, during the 1980s, interest rates in the U.S. reached record highs due to high inflation. In contrast, the 2008 financial crisis led to historically low rates as central banks implemented measures to stimulate economic recovery.
Key Historical Moments
- 1980s: High inflation drives interest rates to double-digit levels, reflecting the challenges of managing economic stability during turbulent times.
- 2008: The global financial crisis results in near-zero interest rates as central banks take unprecedented steps to stabilize the economy.
- 2020s: Central banks respond to the pandemic with extensive monetary easing, highlighting the importance of adaptive policies in addressing unforeseen economic disruptions.
Future Outlook on Interest Rates
The future trajectory of interest rates remains uncertain, contingent on a wide range of economic factors and policy decisions. However, most economists anticipate that rates will remain relatively low in the near term, reflecting ongoing recovery efforts from the pandemic and addressing global economic challenges.
Predictions for the Next Decade
Experts predict that:
- Central banks will gradually raise rates: As economies recover, central banks are expected to incrementally increase interest rates to maintain economic balance.
- Monetary policy will focus on balancing inflation and growth: Policymakers will continue to prioritize managing inflation while fostering sustainable economic growth.
- New technologies and global trends will influence interest rate dynamics: The evolving landscape of technology and global trends may introduce new factors affecting interest rate behavior, requiring adaptive strategies from financial institutions and consumers alike.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
In conclusion, interest rates are a foundational aspect of the financial system, influencing everything from personal savings to global economic policies. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of how interest rates work and their impact on your finances, you can make more informed decisions to achieve your financial objectives and secure long-term stability.
Key takeaways:
- Interest rates are expressed as an annual percentage rate and can be fixed or variable, offering flexibility in financial planning.
- They are shaped by economic conditions, inflation, and central bank policies, reflecting the dynamic nature of the financial system.
- Managing interest rates effectively can help you save money, reduce debt, and grow your wealth, empowering you to achieve your financial goals.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from understanding interest rates. For more insights on personal finance and economics, explore our other articles and resources. Your feedback is invaluable, so feel free to leave a comment or question below!
For further reading, consider consulting authoritative sources such as the Federal Reserve, International Monetary Fund, and World Bank for the latest information on global interest rate trends and economic developments.
![Buying a Home? Mortgage Rate Guide for Singapore [2023]](https://blog.roshi.sg/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Singapore-Home-Loan-Rates-2022.jpeg)